Comparing Rapid Tool Prototyping and Prototyping for Production
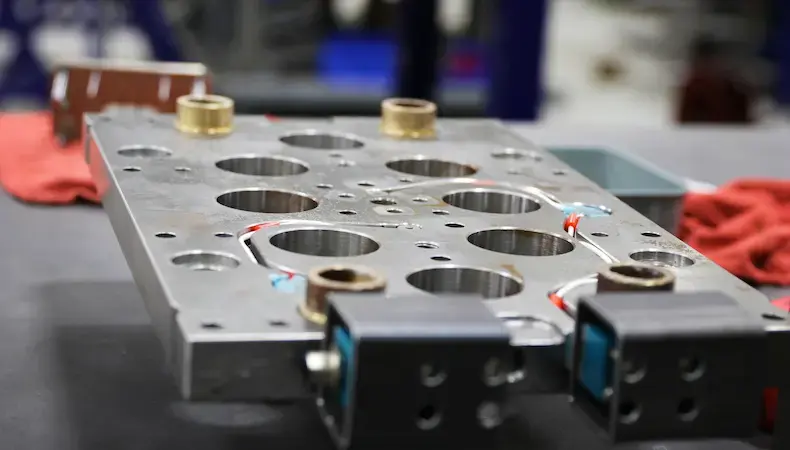
Prototyping an injection-molded component is necessary to ensure proper quality and performance. Rapid tool prototyping and prototyping for injection molding production are two standard prototyping options, and each has its own advantages — but which is right for your projects?
To answer this question and others you may have, we put together a brief comparison of the two approaches.
Rapid Tool Prototyping
Focused on fast turnaround and cost efficiencies, rapid tool prototyping is a solution that uses your CAD file specifications to get a molded part in your hands quickly for an initial evaluation.
The question then becomes one of confidence in parts from a hastily made tool. The primary concern is injection-molded part quality. Provided your prototype tool is ready for full production — and that’s a risky assumption since it hasn’t been fully tested — you may achieve acceptable or even good results with rapid tool prototyping. However, overall injection-molded part quality will likely fall short in consistency and performance.
There’s also cost to consider: What you pocket in upfront savings with rapid tool prototyping could easily be funneled into tooling changes further along in production, when costly defects or process failures are detected. Add the fact that rapid prototype tools offer limited modification options, and the fast-and-inexpensive solution can easily become anything but.
Prototyping for Injection Molding Production
Unlike rapid tool prototyping, the process of prototyping for injection molding production is based on a series of deliberate decisions facilitated by an experienced custom injection molder.
The process hinges on the development of a single-cavity pre-production tool that can be tested. The concept is similar to Design for Manufacturability (DfM) in that prototyping for production provides tangible insights that prove out the design or, conversely, reveal needed improvements.
Parts from the pre-production tool can be physically subjected to testing the variables that typically affect the final shape and function of an injection-molded part. As such, modifications can be made on the front end of design — saving considerable time and money. Since testing and changes are incremental, the ramp-up to full production volume is also done in phases. This maximizes part quality and performance, and virtually eliminates the possibility of unanticipated line shutdown due to defects.
Further, prototyping for production provides an opportunity for OEMs to align with experienced custom injection molders whose design and engineering teams are invested in being true development partners.
Kaysun, for example, is expert in scientific molding and other detailed processes for systematic project improvements, as well as proven in plastics selection. Taken in total, these benefits strengthen prototyping for production and, by extension, injection molding outcomes that can’t necessarily be accomplished through rapid prototyping.
Learn more about the importance of injection molding manufacturing pre-production methods in our infographic, The Process of Scientifically Qualifying a Tool. Click the button below to access your copy now.
Subscribe
TO OUR BLOG

How Do Injection Molder Partnerships Influence Project Costs?
You Might Also Like...
Injection Molding Quotes: 5 Tips to Help Get Tooling Right
Few things impact injection-molded part quality as much as tooling design, materia…
READ MORE

Tooling Audits & Evaluations: How Molders Help OEMs Gauge Health of Assets
When an OEM pursues an injection molding program, tooling is among the most highly…
READ MORE

How Concurrent Design Review Aligns Injection Molding Tooling and Parts [VIDEO]
Tool design is an essential and sometimes underestimated part of injection molding…
READ MORE
