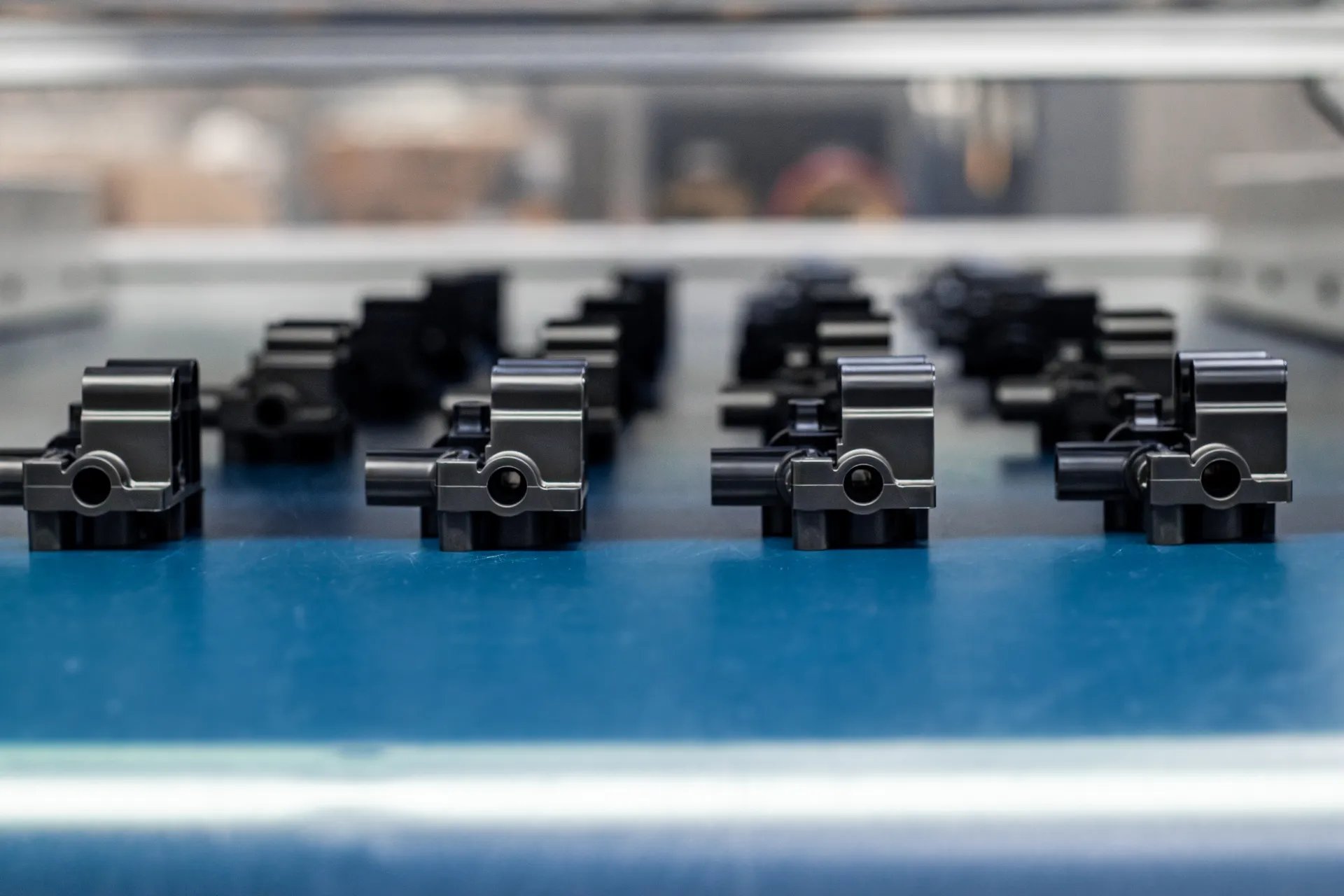

Custom Injection Molding
Custom plastic injection molding is commonly used to produce complex parts for many types of applications, driving a global market value projected to reach nearly $477 billion by 2028. Manufacturers across a range of industries continue to innovate around proven and emerging benefits of plastics and injection molding technology, seeking answers to complicated challenges and customer demands.
What is Injection Molding
The worldwide availability of molding methods may suggest that any injection molding process is a good one, but strategic manufacturers understand that the types of molding and services offered vary greatly.
Commodity molders may be able to quickly produce “custom” low-quality parts at attractive price points. However, plastic injection molders that specialize in ultra-advanced processes and production are relied upon to create individualized solutions for industries including medical, automotive, consumer, and industrial.
Custom plastic injection molding for these complex applications in specialized markets demands scientific processes, analytical tools, and advanced molding technologies – and not all molders have what it takes. Meeting precision and performance standards for these applications requires molder expertise and focus in four key stages of product development:
- Part design
- Material selection
- Tool design
- Process control — scientific molding, insert molding, overmolding, etc.
Partnering with the right injection molder and leveraging key processes gives manufacturers a competitive advantage in the near and long term.



Want more information on the injection molding process?
READ THESE HELPFUL BLOG ARTICLES:

Types of Molding Methods
Not every injection molder is qualified to engineer sophisticated injection molded plastic parts and components. The same can be said for other molding methods which, in comparison to custom injection molding, are limited:
Plastic is heated and inflated with air until it conforms to the shape of a mold to create hollow, thin-walled objects, which is ideal for mass-produced items like plastic bottles and containers, or children’s toys.
Heated plastic is placed in a heated mold, then squeezed — or compressed — into the desired shape. Since advanced composites are often used with this process, compression molding generally produces sturdy, durable parts that can maintain the integrity and shape of parts of varying thicknesses, shapes, and lengths.
The extrusion process consists of pushing melted plastic directly through a die and the product takes on the die’s shape. This method is often used for producing parts requiring continuous length and/or uniform cross sections, such as pipes of different configurations (straight, T-sections, circles, etc.)
“Rotomolding” uses high temperatures and the spinning motion of a mold to distribute melted plastic throughout a mold cavity in order to create large, hollow shapes such as drums, tanks, or recreational equipment like kayaks that require strong, even walls. Rotomolding is a slow process but is very efficient from a materials-use perspective.
Both similar and dissimilar to injection molding, 3D printing gives engineers the power to create plastic designs at their desks in a matter of hours. Further, the process is suited for quick-turn, low-volume, small-scale projects that may have a series of design changes. However, 3D printing cannot adequately replace the precision and robustness of custom plastic injection molding.

How can custom injection molding benefit your application?
FIND OUT IN THESE POPULAR BLOG POSTS:
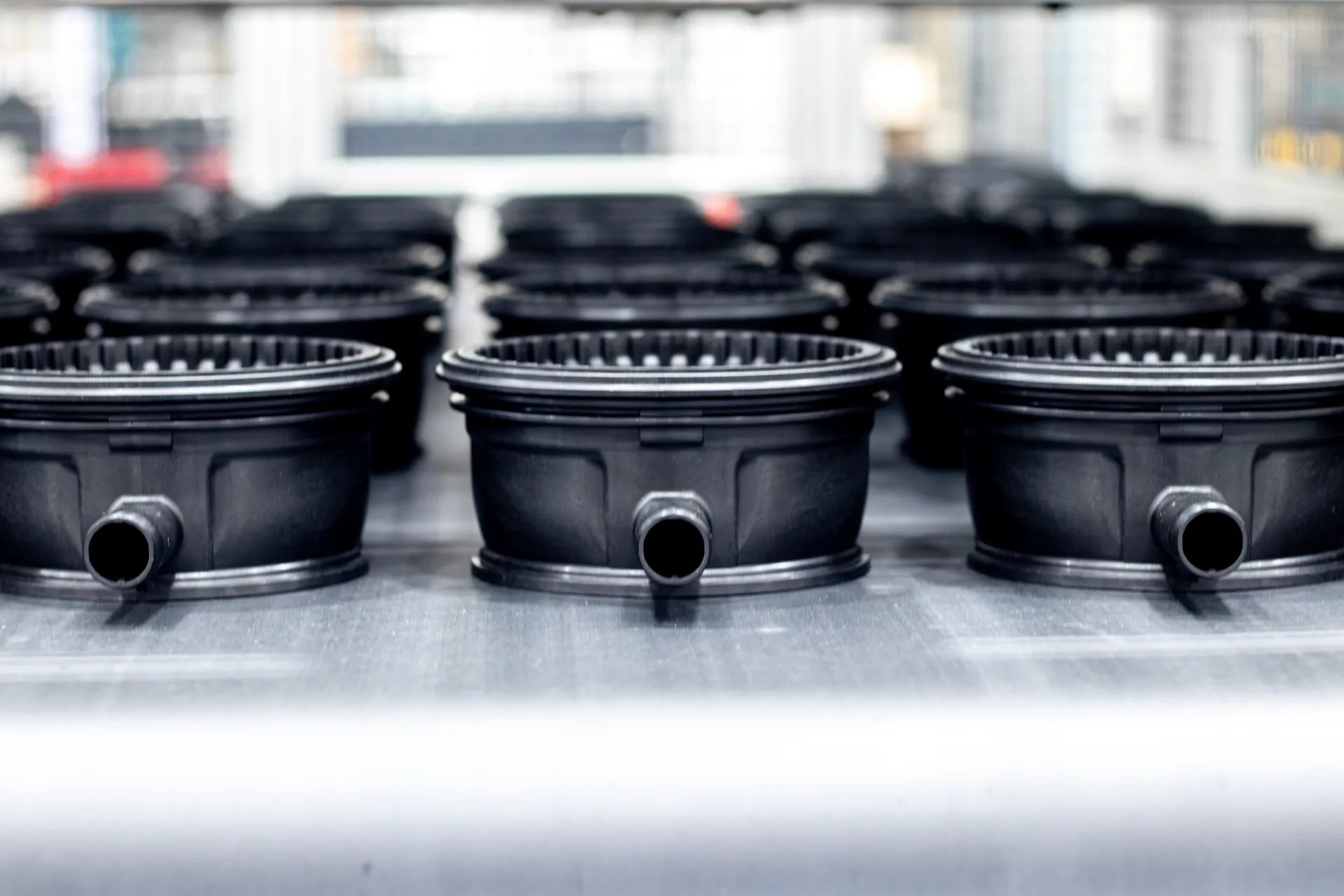

Benefits of Custom Plastic
Injection Molding for Complex Applications
OEMs have options when it comes to molding, but project expectations and functionality often drive the choice in direct proportion to molder capabilities.
For manufacturers with project-specific needs, complex geometries, or any other detailed challenges, custom plastic injection molding provides numerous advantages:
For OEMs with complex part designs requiring tight tolerances, custom plastic injection molders can achieve repeatable design accuracy to within +/- .001 inches.
There are many types of engineering-grade plastics to choose from to produce injection molded plastic parts and components, allowing OEMs to find exactly the right options for their applications and operating environments.
Complex applications require a repeatable process in order to achieve consistent product quality and performance. Custom plastic injection molding uses the same tool for each part, and scientific molding sensors are commonly used to monitor the activity inside the tool for reliable high-output production.
It’s not uncommon for complex part designs to require components made of different materials. The expertise from the molder’s plastics engineers can help ensure that different polymers are compatible under all conditions to help reduce defects.
From the automotive industry to military applications, many OEMs use plastic to help reduce the weight of their products. Today, high-strength, lightweight thermoplastics replace metal components with virtually no difference in strength or dependability.
From matte finishes and unique textures to engraving, injection molding allows for the inclusion of a variety of surface finishes without the need for secondary operations.
Custom or common colors can be added to the injection molding mix. Multiple colors can be used on a single product when two-shot or overmolding processes are used.
Utilizing tools and technologies such as upfront design analysis and support and mold fill analysis software, experienced custom injection molders significantly reduce the number of problems in part design well before production starts — maximizing moldability and minimizing the need for expensive tooling changes. These efficiencies shorten product development timelines, generally reduce project costs, and help get defect-free products to market faster.
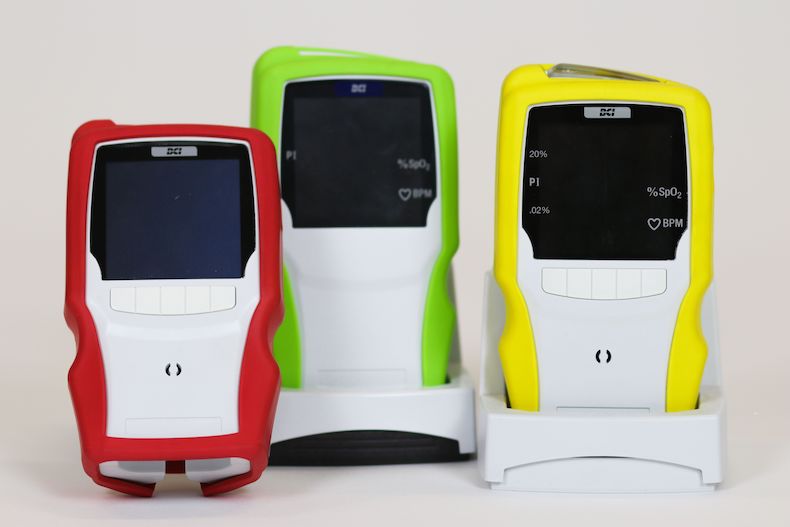

FIND OUT WHY PARTNERING WITH THE RIGHT INJECTION MOLDER IS CRITICAL FOR PROJECT SUCCESS IN THESE INSIGHTFUL ARTICLES:
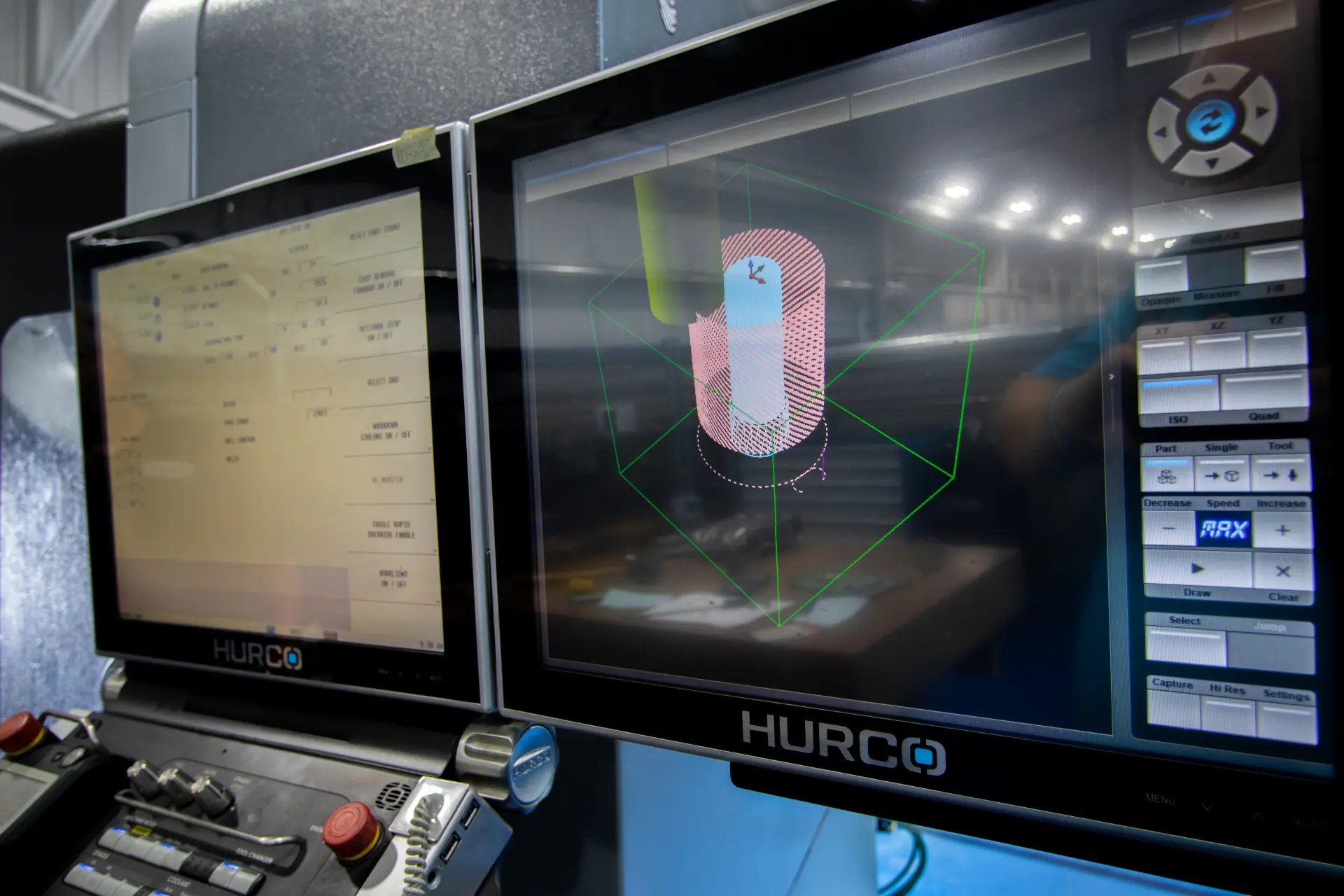

Optimizing the Injection Molding Process
Partnering with a custom injection molder, like Kaysun, with the experience and insights to drive improvements in complex applications – from the product design phase through production – allows opportunities for process optimization through:
The process of consciously and proactively designing parts to optimize all facets of manufacturing, including injection molding.
Specialized DfM engineers align engineering and production in the initial design phase so potential moldability issues, tooling modifications, material selection and substitutions, and other cost and production efficiencies can be identified and resolved before they result in costly rework.
A combination of material science and precise measurement specialized engineers use to completely discern – down to the molecular level – what’s happening during every stage of the injection molding process. Fully understanding how all the different parameters interact in detail helps ensure that high precision is maintained across multiple production runs. Because all the data is recorded, it is easy to replicate the manufacturing process as needed, even when production is transferred from one machine to another, saving a tremendous amount of setup time.
A sophisticated computer program that analyzes and predicts the flow and cooling of plastic during all phases of the injection molding process. Levels of mold filling analysis vary from simulating fill and packing phases to optimize gate location, gate sizes, and process conditions, through more advanced simulations comparing runner systems, mold temperatures, and fiber orientation to gauge shrink and warp.
Plastic Injection
Molding Applications
Ideal projects include but aren’t limited to:
- Large annual volume productions that justify the tooling investment
- Component design geometries that involve complex designs and shapes
- Complex applications that require precision, extremely tight tolerances and/or a consistent, exceedingly high level of quality
- Part consolidation or metal-to-plastic conversion opportunities that streamline production and/or address industry mandates, such as vehicle lightweighting requirements implemented in the auto industry
- Applications constructed from expensive material(s) that would result in excessive waste and significant budgetary concerns if machined
- Projects in which the part design will not change over several years, thereby maximizing the value of the tooling investment
-
Applications in which surface finish is a factor, as injection molding can yield a wide variety of textured or engraved surfaces
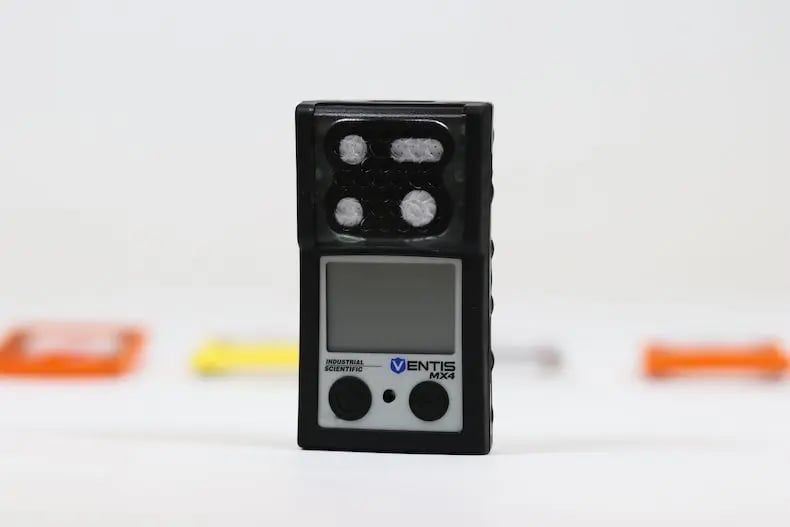


Tight Tolerances
Tight tolerances frequently top an OEM’s list of factors that impact projects and also influence injection molder selection. As such, it’s worth noting how potential injection molding partners approach tight tolerances during the project design phase.
A molder with the know-how and willingness to explore all aspects of the design is essential, and one that asks the tough questions upfront will contribute to successful outcomes.
part performance, longevity and appearance?
Many designers automatically set a tolerance in the CAD drafting software and all dimensions are toleranced to that number, when in reality the product may not need such a tight tolerance.
Physical part size also affects tight tolerance capability. Large parts are difficult to hold to tight tolerances consistently. Local areas within the large part, however, are easier to manage and can be dimensioned accordingly.
behavior and tolerance?
Plastics typically have large thermal expansion coefficients; as a result, tight-tolerance parts may have to be measured at a consistent temperature.
thickness variations impact
outcomes?
Exposure to temperature fluctuation in normal operation may cause part expansion or contraction that makes tight tolerance unnecessary. Or, some plastic parts — especially those made from nylon — lose some of their dimensional stability when they leave a tightly controlled atmosphere and are used in environments with higher moisture content.
In order to truly benefit from all of these advantages, it’s important that manufacturers seek out experienced custom plastic injection molders that know how to maximize efficiency and overcome any design or process issues.
Having the best equipment, technology, and materials will only get you so far; it’s having the best, most experienced engineers and tooling partners that really makes a difference in lead times, costs, and final quality.
TAKE A LOOK AT THESE ARTICLES TO LEARN MORE ABOUT TIGHT TOLERANCES:

Injection Molder
Certifications
In addition to project specifics, OEMs in medical, automotive, consumer, and industrial markets need to verify a custom plastic injection molder’s credentials before assigning projects, many times helping to ensure their inclusion on an approved vendor list.
Holding industry-specific certifications — ISO, ITAR, IATF, MedAccred, etc. — does more than provide credibility to injection molders. It ensures the highest standards are maintained during all project phases and OEMs are in compliance with their respective industry mandates.
Learn more about custom injection molding for complex applications in these popular blog articles:

Injection Molding Technology & Key Processes
Custom plastic injection molding is remarkably versatile. OEMs often gain efficiencies — and usually cost savings — from the experience full-service injection molders are able to provide.
Multi-material molding allows for the integration of additional materials — polymers, metals, and other non-plastics — during molding to add features and simplify assembly. Popular methods of multi-material molding include:
Overmolding (Multi-Shot Molding)
Overmolding, also referred to as multi-shot molding, is a unique injection molding process that results in a seamless combination of multiple materials into a single part or product. It typically includes a rigid, plastic-base component overlaid with a thin, pliable, rubber-like thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) exterior layer or other materials using either a single- or two-shot technique to:
- Improve product performance since TPE creates soft surfaces, good grip, and an environmental barrier against shock, vibration, noise, electrical interference, and chemical/UV intrusion
- Increase shelf appeal with the desired look that helps a product stand out from the competition since TPE can be used to create a visually attractive surface that includes myriad colors and textures
- Lower production costs by reducing the number of manufacturing steps involved
Insert Molding
There is a perception that insert molding is used to merely create plastic-covered metal cylinders to bolt to brackets, mounts, or other components. While this definition is accurate, it’s also narrow. Bearings, custom stampings, flexible circuits, and parts made from powdered metal, rubber, or other materials can be insert-molded as single parts. They could also be combined and configured inside the tool and then sealed together with the plastic during the insert-molding process.
Although a custom-made tool that accepts the proposed insert(s) is necessary, the tradeoff in benefits is well worth the investment, since insert molding realizes:
- Improved manufacturability by replacing some post-tool assembly operations such as snap fits, gluing, and the use of screws or other fasteners
- Cost savings with part number reductions, supplier consolidation, and part tracking and shipping
- Stronger and more consistent parts compared to those created using secondary operations and manual insertions instead of automated processes offered by some injection molders
For more on overmolding, read these valuable blog posts:
Metal-to-plastic conversion uses engineered plastics with properties similar — or superior — to metal to improve product or component integrity while also providing:
- Tensile strength comparable to metal
- Reduced part weight
- A highly repeatable process (less scrap)
- Lower manufacturing costs
- Enhanced regulatory compliance
- Greater design flexibility
- Increased market stability for material cost
- Lower packaging and shipping costs
- Lower finishing costs (pre-color, surface finish)
Read through these blog posts to learn more about metal-to-plastic conversion:
How To Select the
Right Partner for Your
Complex Application

Use this checklist to find your best fit:
Plastics engineering experts with a proven track record of successes
Dedicated to molder-customer collaboration from project inception through production
Adds value that positively impacts manufacturers’ bottom lines
Offers supply chain stability and on time delivery

Does your company fit our ideal customer profile?
Complete the form to request a free consultation with our plastic engineering experts.